| EPHA4 |
|---|
 |
| Available structures |
|---|
| PDB | Ortholog search: PDBe RCSB |
|---|
| List of PDB id codes |
|---|
2LW8, 2WO1, 2WO2, 2WO3, 3CKH, 3GXU, 4BK4, 4BK5, 4BKA, 4BKF, 4M4P, 4M4R, 4W4Z, 4W50, 5JR2 |
|
|
| Identifiers |
|---|
| Aliases | EPHA4, Epha4, 2900005C20Rik, AI385584, Cek8, Hek8, Sek, Sek1, Tyro1, rb, EPH receptor A4, HEK8, SEK, TYRO1, EK8 |
|---|
| External IDs | OMIM: 602188 MGI: 98277 HomoloGene: 20933 GeneCards: EPHA4 |
|---|
| Gene location (Human) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 2 (human)[1] |
|---|
| | Band | 2q36.1 | Start | 221,418,027 bp[1] |
|---|
| End | 221,574,202 bp[1] |
|---|
|
| Gene location (Mouse) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 1 (mouse)[2] |
|---|
| | Band | 1 C4|1 39.55 cM | Start | 77,343,822 bp[2] |
|---|
| End | 77,491,725 bp[2] |
|---|
|
| RNA expression pattern |
|---|
| Bgee | | Human | Mouse (ortholog) |
|---|
| Top expressed in | - Brodmann area 23
- frontal pole
- middle temporal gyrus
- endothelial cell
- superior frontal gyrus
- parietal lobe
- postcentral gyrus
- palpebral conjunctiva
- nipple
- entorhinal cortex
|
| | Top expressed in | - medial ganglionic eminence
- medial dorsal nucleus
- lateral geniculate nucleus
- nucleus accumbens
- primary motor cortex
- hippocampus proper
- prefrontal cortex
- medial geniculate nucleus
- Region I of hippocampus proper
- subiculum
|
| | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
| BioGPS | 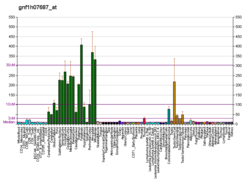
 | | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
|
| Gene ontology |
|---|
| Molecular function | - transferase activity
- protein kinase activity
- nucleotide binding
- GPI-linked ephrin receptor activity
- ephrin receptor binding
- DH domain binding
- transmembrane-ephrin receptor activity
- kinase activity
- protein binding
- identical protein binding
- transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase activity
- PH domain binding
- protein tyrosine kinase activity
- ATP binding
- ephrin receptor activity
- amyloid-beta binding
- protein tyrosine kinase binding
| | Cellular component | - cytoplasm
- axon terminus
- integral component of membrane
- cell body
- perikaryon
- postsynaptic membrane
- Golgi apparatus
- endosome
- cell projection
- early endosome membrane
- membrane
- postsynaptic density
- filopodium
- neuromuscular junction
- plasma membrane
- dendritic spine
- axonal growth cone
- integral component of plasma membrane
- synapse
- cell surface
- mitochondrial outer membrane
- cell junction
- axon
- dendrite
- early endosome
- endoplasmic reticulum
- neuron projection
- dendritic shaft
- receptor complex
- Schaffer collateral - CA1 synapse
- glutamatergic synapse
- integral component of postsynaptic membrane
- integral component of presynaptic membrane
| | Biological process | - negative regulation of axon regeneration
- fasciculation of motor neuron axon
- phosphorylation
- transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway
- positive regulation of JUN kinase activity
- regulation of GTPase activity
- nervous system development
- regulation of axonogenesis
- multicellular organism development
- protein phosphorylation
- regulation of astrocyte differentiation
- cell adhesion
- positive regulation of dendrite morphogenesis
- nephric duct morphogenesis
- protein autophosphorylation
- corticospinal tract morphogenesis
- peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation
- fasciculation of sensory neuron axon
- motor neuron axon guidance
- positive regulation of Rho guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity
- regulation of dendritic spine morphogenesis
- glial cell migration
- adult walking behavior
- axon guidance
- ephrin receptor signaling pathway
- negative regulation of neuron projection development
- protein stabilization
- positive regulation of protein tyrosine kinase activity
- neuron projection guidance
- synapse pruning
- neuron projection fasciculation
- negative regulation of long-term synaptic potentiation
- positive regulation of amyloid-beta formation
- positive regulation of aspartic-type endopeptidase activity involved in amyloid precursor protein catabolic process
- negative regulation of proteolysis involved in cellular protein catabolic process
- cellular response to amyloid-beta
- regulation of modification of synaptic structure
| | Sources:Amigo / QuickGO |
|
| Orthologs |
|---|
| Species | Human | Mouse |
|---|
| Entrez | | |
|---|
| Ensembl | | |
|---|
| UniProt | | |
|---|
| RefSeq (mRNA) | |
|---|
NM_001304536
NM_001304537
NM_004438
NM_001363748 |
| |
|---|
| RefSeq (protein) | |
|---|
NP_001291465
NP_001291466
NP_004429
NP_001350677 |
| |
|---|
| Location (UCSC) | Chr 2: 221.42 – 221.57 Mb | Chr 1: 77.34 – 77.49 Mb |
|---|
| PubMed search | [3] | [4] |
|---|
|
| Wikidata |
| View/Edit Human | View/Edit Mouse |
|

 1b0x: THE CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF AN EPH RECEPTOR SAM DOMAIN REVEALS A MECHANISM FOR MODULAR DIMERIZATION.
1b0x: THE CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF AN EPH RECEPTOR SAM DOMAIN REVEALS A MECHANISM FOR MODULAR DIMERIZATION. 2hel: Crystal structure of a mutant EphA4 kinase domain (Y742A)
2hel: Crystal structure of a mutant EphA4 kinase domain (Y742A)






















