| DCLK1 |
|---|
|
| Available structures |
|---|
| PDB | Ortholog search: PDBe RCSB |
|---|
| List of PDB id codes |
|---|
1MFW, 1MG4, 1UF0 |
|
|
| Identifiers |
|---|
| Aliases | DCLK1, CL1, CLICK1, DCAMKL1, DCDC3A, DCLK, doublecortin like kinase 1 |
|---|
| External IDs | OMIM: 604742; MGI: 1330861; HomoloGene: 130530; GeneCards: DCLK1; OMA:DCLK1 - orthologs |
|---|
| Gene location (Human) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 13 (human)[1] |
|---|
| | Band | 13q13.3 | Start | 35,768,652 bp[1] |
|---|
| End | 36,131,382 bp[1] |
|---|
|
| Gene location (Mouse) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 3 (mouse)[2] |
|---|
| | Band | 3|3 C | Start | 55,149,785 bp[2] |
|---|
| End | 55,446,489 bp[2] |
|---|
|
| RNA expression pattern |
|---|
| Bgee | | Human | Mouse (ortholog) |
|---|
| Top expressed in | - endothelial cell
- frontal pole
- Brodmann area 10
- Brodmann area 23
- pars reticulata
- Pars compacta
- occipital lobe
- middle temporal gyrus
- superior vestibular nucleus
- primary visual cortex
|
| | Top expressed in | - stria vascularis
- piriform cortex
- habenula
- visual cortex
- superior frontal gyrus
- primary motor cortex
- prefrontal cortex
- olfactory tubercle
- temporal lobe
- subiculum
|
| | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
| BioGPS | 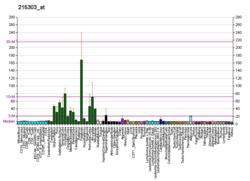
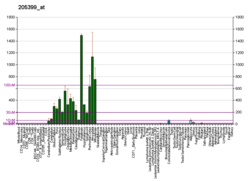 | | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
|
| Gene ontology |
|---|
| Molecular function | - transferase activity
- protein kinase activity
- nucleotide binding
- kinase activity
- ATP binding
- protein serine/threonine kinase activity
| | Cellular component | - integral component of plasma membrane
- intracellular anatomical structure
- postsynaptic density
| | Biological process | - cell differentiation
- axonogenesis
- dendrite morphogenesis
- phosphorylation
- response to virus
- neuron migration
- nervous system development
- multicellular organism development
- endosomal transport
- protein phosphorylation
- central nervous system development
- brain development
- axon extension
- forebrain development
- central nervous system projection neuron axonogenesis
- negative regulation of protein localization to nucleus
- peptidyl-serine phosphorylation
- peptidyl-threonine phosphorylation
- intracellular signal transduction
- neuron projection morphogenesis
| | Sources:Amigo / QuickGO |
|
| Orthologs |
|---|
| Species | Human | Mouse |
|---|
| Entrez | | |
|---|
| Ensembl | | |
|---|
| UniProt | | |
|---|
| RefSeq (mRNA) | NM_001195415
NM_001195416
NM_001195430
NM_004734
NM_001330071
|
|---|
NM_001330072 |
| NM_001111051
NM_001111052
NM_001111053
NM_001195538
NM_001195539
|
|---|
NM_001195540
NM_019978
NM_001357466
NM_001357468
NM_001357469
NM_001357475
NM_001357476 |
|
|---|
| RefSeq (protein) | NP_001182344
NP_001182345
NP_001182359
NP_001317000
NP_001317001
|
|---|
NP_004725 |
| NP_001104521
NP_001104522
NP_001104523
NP_001182467
NP_001182468
|
|---|
NP_001182469
NP_064362
NP_001344395
NP_001344397
NP_001344398
NP_001344404
NP_001344405 |
|
|---|
| Location (UCSC) | Chr 13: 35.77 – 36.13 Mb | Chr 3: 55.15 – 55.45 Mb |
|---|
| PubMed search | [3] | [4] |
|---|
|
| Wikidata |
| View/Edit Human | View/Edit Mouse |
|
 1mfw: STRUCTURE OF N-TERMINAL DOUBLECORTIN DOMAIN FROM DCLK: SELENOMETHIONINE LABELED PROTEIN
1mfw: STRUCTURE OF N-TERMINAL DOUBLECORTIN DOMAIN FROM DCLK: SELENOMETHIONINE LABELED PROTEIN 1mg4: STRUCTURE OF N-TERMINAL DOUBLECORTIN DOMAIN FROM DCLK: WILD TYPE PROTEIN
1mg4: STRUCTURE OF N-TERMINAL DOUBLECORTIN DOMAIN FROM DCLK: WILD TYPE PROTEIN 1uf0: Solution structure of the N-terminal DCX domain of human doublecortin-like kinase
1uf0: Solution structure of the N-terminal DCX domain of human doublecortin-like kinase






















