| POU5F1 |
|---|
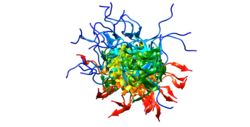 |
| Visualisation de la protéine Cristallisée OCT4 |
| Structures disponibles |
|---|
| PDB | Recherche d'orthologue: PDBe RCSB |
|---|
| Identifiants PDB |
|---|
1OCP, 3L1P |
|
|
| Identifiants |
|---|
| Aliases | POU5F1, OCT4, Octamer-binding transcription factor 4 |
|---|
| IDs externes | OMIM: 164177 MGI: 101893 HomoloGene: 8422 GeneCards: POU5F1 |
|---|
| Position du gène (Homme) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 6 humain[1] |
|---|
| | Locus | 6p21.33 | Début | 31,164,337 bp[1] |
|---|
| Fin | 31,180,731 bp[1] |
|---|
|
| Position du gène (Souris) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 17 (souris)[2] |
|---|
| | Locus | 17 B1|17 18.69 cM | Début | 35,816,915 bp[2] |
|---|
| Fin | 35,821,669 bp[2] |
|---|
|
| Expression génétique |
|---|
| Bgee | | Humain | Souris (orthologue) |
|---|
| Fortement exprimé dans | - gonade
- right uterine tube
- muqueuse utérine
- human kidney
- body of pancreas
- body of stomach
- mucosa of transverse colon
- testicule
- left uterine tube
- fundus
|
| | Fortement exprimé dans | - blastocyste
- Épiblaste
- embryon
- morula
- morula
- primordial germ cell
- zygote
- masse cellulaire interne
- ligne primitive
- ooblast
|
| | Plus de données d'expression de référence |
|
|---|
| BioGPS | 
 | | Plus de données d'expression de référence |
|
|---|
|
| Gene Ontology |
|---|
| Fonction moléculaire | - liaison ADN
- sequence-specific DNA binding
- liaison miARN
- DNA-binding transcription factor activity
- transcription factor binding
- transcription cis-regulatory region binding
- liaison protéique
- DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific
- DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific
- ubiquitin protein ligase binding
- liaison ARN
| | Composant cellulaire | - cytoplasme
- cytosol
- transcription regulator complex
- nucléoplasme
- noyau
- mitochondrie
| | Processus biologique | - regulation of transcription, DNA-templated
- somatic stem cell population maintenance
- negative regulation of gene silencing by miRNA
- cell fate commitment involved in formation of primary germ layer
- endodermal cell fate specification
- morphogenèse d'une structure anatomique
- mRNA transcription by RNA polymerase II
- regulation of asymmetric cell division
- negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II
- transcription by RNA polymerase II
- transcription, DNA-templated
- regulation of DNA methylation-dependent heterochromatin assembly
- développent d'un organisme multicellulaire
- cardiac cell fate determination
- response to wounding
- BMP signaling pathway involved in heart induction
- régulation de l'expression des gènes
- regulation of heart induction by regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway
- blastocyst development
- positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II
- positive regulation of SMAD protein signal transduction
| | Sources:Amigo / QuickGO |
|
| Orthologues |
|---|
| Espèces | Homme | Souris |
|---|
| Entrez | | |
|---|
| Ensembl | ENSG00000230336
ENSG00000206454
ENSG00000204531
ENSG00000237582
ENSG00000229094
|
|---|
ENSG00000233911
ENSG00000235068 |
| |
|---|
| UniProt | | |
|---|
| RefSeq (mRNA) | |
|---|
NM_203289
NM_001173531
NM_001285986
NM_001285987
NM_002701 |
| |
|---|
| RefSeq (protéine) | NP_001167002
NP_001272915
NP_001272916
NP_002692
NP_976034
|
|---|
NP_001272915.1 |
| |
|---|
| Localisation (UCSC) | Chr 6: 31.16 – 31.18 Mb | Chr 17: 35.82 – 35.82 Mb |
|---|
| Publication PubMed | [3] | [4] |
|---|
|
| Wikidata |
| Voir/Editer Humain | Voir/Editer Souris |
|

 Portail de la médecine
Portail de la médecine  Portail de la biologie cellulaire et moléculaire
Portail de la biologie cellulaire et moléculaire 




















